If you were a tourist in Florida in 2016, you might have been disappointed. Massive algae blooms surfaced along the east coast, and Gov. Rick Scott declared a state of emergency and closed all beaches in three counties. The problem returned in 2018, but worse: beaches on both coasts were closed and invasive, toxic, blue-green algae choked many freshwater lakes, rivers and residential waterways.
The freshwater problem originated in Lake Okeechobee, the largest lake in Florida. Massive rainfall that year required the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, which manages the lake’s levels, to discharge billions of gallons of water to prevent flooding. The water coursed through the Caloosahatchee and St. Lucie Rivers, bringing with it rich nutrients that fueled algae overgrowth downstream.
An increasing problem
Dense blooms block sunlight from reaching underwater plants and animals, and can clog the gills of fish and other aquatic animals, so they can’t breathe. When the bloom dies off and decays, it uses up oxygen in the water, killing fish and producing noxious odors. Some bloom-forming algae produce potent toxins that can harm the health of humans and land animals as well.
HABs also pose a severe problem for drinking water reservoirs because the toxins are challenging to treat, and the algae can affect treatment processes. Sometimes treatment can produce potable water, but if it doesn’t, affected water districts must provide bottled water to customers for drinking. In 2019, the California Dept. of Water Resources (water.ca.gov) reported, “Common water purification techniques such as camping filters, tablets and boiling don’t remove toxins.”
Existing approaches
How can dangerous HABs be treated or controlled? In one of four ways, according to the U.S. National Office for Harmful Algal Blooms (hab.whoi.edu):
• Environmental—These methods change the habitat that favor HABs, for example, by controlling the nitrogen and phosphorus pollution that feeds the blooms, or by further circulating the water;
• Biological—In some cases, a parasite can kill the algae, but the long-term effects of introducing the parasite in the water are unclear;
• Chemical—Sprinkling the water’s surface with copper sulfate is a common chemical method, which kills the algae, but it’s toxic to fish; and
• Physical or mechanical—Clay can be spread on the water’s surface, and the tiny, dense clay particles combine with other particles in the water, including algae cells, and then sink to the bottom.
These methods can be effective, but they have drawbacks. Environmental treatments are important for the future, especially to reduce the nutrient pollution that feeds algal blooms, but they take time and require legislation or regulatory changes for industry, farmers and ranchers, and residents. Biological treatments have long-term risks because their future effects are largely unknown.
Chemical treatments may be toxic to fish, and both chemical and physical treatments just push algae to the bottom, where they decompose. But algae cells contain about 70% carbon, and can release methane when they decay. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas (GHG) that warms the atmosphere 80 times more than carbon dioxide in the short term. Even though the algae are killed, the nutrients remain, so the problem comes back quickly and often to a greater degree than before the treatment.
Focus on infrastructure
Aecom often coordinates with universities and government agencies due to the size of its projects. Levy and Bill Colona, Aecom’s operations manager for algae, have made it their mission to develop technologies that can mitigate and restore nutrient-impacted waterways. When it came to the recent algal blooms, they collaborated with David Pinelli, president of Ecosa Process Technologies and a technical expert in liquid/solid separation systems.
Pinelli previously worked at a company developing algae-based bio-foam to replace commercial plastics, and he knew that the process he developed for recovering algae could be effectively scaled. Levy recognized this could be an innovative solution for waterways, and he and Pinelli collaborated to develop their patent-pending Hydronucleation Flotation Technology (HFT) for harvesting algae.
HFT separates algae from water without rupturing the algae cells—a key point because algae cells release toxins when ruptured. Because algae contains nutrients, the process also removes the nutrients, so they can’t trigger another bloom.
Chetrit is a mechanical engineer, who knows the value of automation. He was first exposed to Opto 22 hardware more than 20 years ago, and kept up with the company’s technology through various projects. For the algae harvester design, he chose Opto 22’s groovEPIC edge-programmable industrial computer.
Despite available technology, there was still a gap in engineering a solution that would work effectively with nature in restoring damaged ecosystems. To address this issue, Levy contacted Dr. Tammy Karst-Riddoch, Aecom's senior limnologist and algae expert.
The process
The resulting process is a solution in which wild algae are harvested using the HFT to gently separate algae from the water column by using extremely small (nano-sized) air bubbles, which take advantage of the algae’s proclivity to float. The HFT prevents damage to the algae cells, and allows efficient removal of nutrients and atmospheric carbon, while preventing the release of cyanotoxins.
The developers report their process is simple and effective:
• Water is pumped from the affected waterway to the HFT. A treatment solution coagulates and flocculates the algae into larger particles before separation.
• The water containing coagulated algae is directed to a flotation chamber. Nano-sized bubbles are introduced into the chamber, and they attach to the algae and carry it to the surface as the bubbles rise. Once enough algae floc has accumulated on the surface, a skimming system physically removes the algae from the water column.
• The clean, clarified water is returned to the environment. The returned water is highly oxygenated from the hydronucleation process, and provides additional benefits by increasing oxygen levels in the waterway, which can be very low in these impacted water bodies.
• The recovered algae biomass, rich in nutrient and carbon, can be transformed into a variety of green products, including biofertilizers, clean energy (both biocrude and biogas), and commercial bio-foam products.
Though environmental conditions (temperatures, turbidity, pH, chlorophylls, dissolved oxygen) vary in HAB-impacted waterways, the HFT can be designed and operated to effectively remove the algae in all cases. For each location, Pinelli uses bench-scale testing techniques, and dials in the appropriate harvester treatment regimen to optimize performance.
Designing the control system
To control its gathering process, collect and distribute data, and provide a user interface for operators and observers, the algae harvester employs a groovEPIC control system. Chetrit has used Opto 22 products for some years and trained on the system.
The harvester’s groovEPIC system consists of an industrial, Linux-based, edge-programmable industrial controller, power supply and the following I/O modules, all mounted on one chassis:
• One 12-channel AC discrete input module;
• One 12-channel DC discrete input module;
• Three eight-channel AC/DC electromechanical relay output modules;
• One 24-channel analog input module;
• One eight-channel analog output module with chassis-powered loop; and
• One four-channel serial communication module.
The system also includes a cellular router for remote access and automated reporting via email. Because groovEPIC handles data communication from the edge of a network to the cloud, it offers built-in security features and connectivity options in addition to controlling the process and communicating with other elements of the overall system.
The program also detects end-of-month events, and starts a new monthly file at that point. Both daily data and cumulative monthly data are stored locally and emailed daily, with a daily summary in the body of the email.
Modbus protocol is used to communicate with the multi-parameter sondes. Separate influent and effluent sondes each include multiple probes that monitor water quality and system performance, including temperature, pH, turbidity, chlorophyll levels and dissolved oxygen. The sondes communicate via a Modbus adapter directly to the serial module on the groovEPIC. The programming controls the sensors’ reading, cleaning and recording cycle.
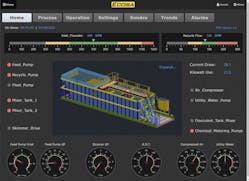
Chetrit reached out to Dave Engsberga, another longtime colleague, and worked with an Opto 22 expert to develop Modbus communications, data handling and emailing charts and subroutines. He built the HMI using groovEPIC’s included groov View software, which is “permission-driven,” he explains, “so an operator sees different screens than someone reviewing data and operations.”
The HMI consists of several types of screens. Operator screens are for setting and operating pumps, pressures, tanks, agitator and the skimmer, which can run continuously or intermittently. Other screens show alarms, power usage, processing, data from the process and sondes, and trends over time.
The HMI is accessed via a panel-mounted touchscreen connected to the HDMI port on the groovEPIC. The HMI can also be accessed remotely via a cellular router.
In groov View, Chetrit adapted all HMI screens to a fully functioning mobile device interface, so operators can use it in the groov View app. The HMI can also be viewed locally and by authorized users on PCs or mobile devices worldwide.
“This equipment is totally accessible for me coming to it as a mechanical engineer,” says Chetrit. “I can build a system without being a system integrator.”
Aecom’s technicians operate each system, and the VPN client on the groovEPIC processor also makes it possible to securely access groovEPIC from just about anywhere.
“They love the remote access, and so do I,” Chetrit says. From his office located in Minnesota, he can log in at any time to any unit in the field, just to check on it or to update its control program or HMI.
The result
The team developed a comprehensive restoration program that can be scaled to any size and used throughout the U.S. and the world. Their technical process has proven to be safe, highly effective and efficient, achieving algae removal percentages in the high 90s.
Meanwhile, to provide a closed-loop system with virtually no waste, Aecom reports that it's alaso been working with other industry leaders to transform the recovered algae into clean, carbon-neutral energy. Aecom conducted its first ever, field-scale, algae-to-fuel demonstration project in Ohio in 2022. The A 1-MGD harvester removed algae from Harsha Lake, a drinking water source and recreational water body near Cincinnati.
The recovered algae was transformed into a biocrude oil using hydrothermal liquefaction. This process uses heat and pressure just like the natural process of producing oil, but it’s completed in 30 minutes instead of the millions of years that nature requires.
“We turned on the harvester at 8:00 a.m. and by noon, we had a biocrude product that can be further processed for fuel,” says Levy.
What’s next?
By harnessing the power of algae to consume nutrients and atmospheric carbon, it’s now possible to remove the key nutrients that fuel HABs by harvesting algae. The harvesters can help restore waterways, decarbonize the planet, and produce a biomass rich in carbon and nutrients that can be converted to clean energy, fertilizer and other products. In March 2022, Aecom formed a partnership with Genifuel to produce aviation fuel from the biomass.
As more harvesters are deployed, Chetrit plans to add cloud-based data processing, onsite video, and other elements to the groovEPIC-based control system. In addition, Aecom recently received an innovation grant to incorporate an intelligent process automation system (IPAS) into the harvester.
To date, the algae harvesters have been designed for fresh water, but as Florida’s experience since 2016 illustrates, harmful algal blooms are also a severe problem in saltwater. Aecom and its team plan to look into similar treatments for brackish water.